Prenatal Visits:
Regular visits to an obstetrician or midwife are essential throughout pregnancy. These visits typically occur monthly in the first trimester, biweekly in the second trimester, and weekly in the third trimester. During these visits, the healthcare provider monitors the mother's health, fetal development, and provides guidance on nutrition, exercise, and any concerns that may arise.
Nutrition:
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and dairy products is crucial for both mother and baby. Folic acid, iron, calcium, and other prenatal vitamins are often recommended to support fetal growth and development.

Exercise:
Regular, moderate exercise during pregnancy can improve mood, reduce discomfort, and promote overall health. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise program and to avoid activities that may pose a risk of injury or strain.
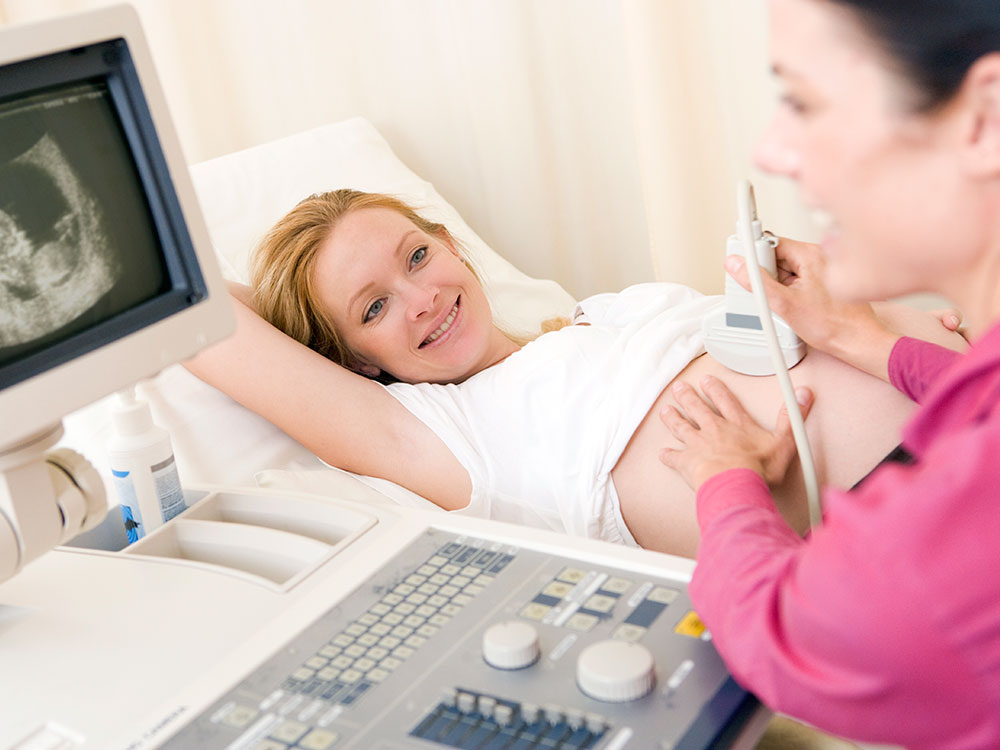
Prenatal Screening and Testing:
Various screenings and tests are offered throughout pregnancy to assess the health of the fetus and identify any potential complications. These may include ultrasound scans, blood tests, and genetic screening for conditions such as Down syndrome.
Education and Preparation:
Expectant parents benefit from education on pregnancy, childbirth, and newborn care. Prenatal classes cover topics such as labor and delivery, breastfeeding, infant care, and postpartum recovery.
Emotional Support:
Pregnancy can bring about a range of emotions, from excitement and joy to anxiety and stress. It's essential for expectant mothers to seek emotional support from partners, family members, friends, or healthcare providers as needed.

Avoiding Harmful Substances:
Smoking, alcohol, and illicit drugs can pose serious risks to fetal development. It's important for expectant mothers to avoid these substances entirely and to minimize exposure to environmental toxins and hazards.
Monitoring for Complications:
Certain conditions, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm labor, require careful monitoring and management during pregnancy. Early detection and intervention can help mitigate risks and improve outcomes for both mother and baby.
Birth Plan:
Developing a birth plan allows expectant parents to communicate their preferences for labor and delivery with their healthcare providers. This may include preferences for pain management, labor positions, and other aspects of the birthing process.
Postpartum Care:
Pregnancy care extends into the postpartum period, encompassing physical recovery, breastfeeding support, and mental health care for both mother and baby.


